Classification of Cities
This classification splits the Chinese market in different levels of developments. It is useful for strategies of business development and market analysis.
The tier 1 cities are Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen.These were the first to be opened up to competitive economic development by the Chinese government, and so are the most populous, affluent and competitive cities in the country.
The tier 2 cities are around 60 cities. Tianjin and Chengdu are growing faster than other cities of this category. These two cities are considered rapidly developing economic centers. Nanjing and Xi’an are growing but less quickly. Wuhan and Hefei were behind but now are developping faster.
The New Consumer
The new consumer class is more likely to consider emotional benefits of the product or service she/he buys and prefer certain brands. She/he will typically be of the younger generation and live in the more developed eastern coastal provinces.
Younger consumers are more likely to imitate the spending habits of consumers in developed countries.
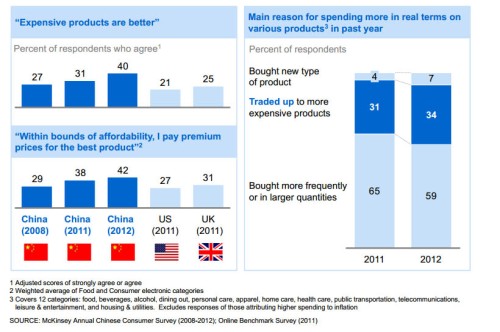
About 41% of younger consumers in this new class are inclined to pay a premium for the best products, compared to 31% of older consumers.
According to McKinsey, the proportion of urban households able to afford cars and small luxuries will rise six-fold in the next decade and account for 57% of the total population by 2020.
It also estimated that the largest 225 cities in China will contribute 27% to global economic growth between 2013 and 2025.
The consumer trend in China’s first-tier cities is quite different from other cities in the country. People in the country’s largest cities typically spend more. For example, they are spending 35% more on dining out than people in second-tier cities, and 50% more than residents of third-tier cities.
Strategies for Economic Development in China



No comments:
Post a Comment